markdown 文章内容
7-1词典 这道题用map写很快的,有些同学是用字符串数组遍历查找做的,数据量大的话会超时,建议大家好好学一下c++,很好用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <iostream> #include <map> using namespace std; int main(){ int n,m; cin>>n>>m; map<string,string>mp; while(n--){ string s1,s2; cin>>s1>>s2; mp[s2]=s1; } while(m--){ string s; cin>>s; if(mp.count(s)) cout<<mp[s]<<endl; else cout<<"eh"<<endl; } return 0; }
7-2镖局运镖 将所有城市连成一个图,要求花费最低,就是在考最小生成树嘛。这里给大家介绍两个算法,kruskal算法和prime算法。
kruskal算法 1、将权重最小的边和两个结点加入树;
2、剩下边中选择权重最小的边,如果两个结点不在同一个连通分支(并查集),就将此边加入树,否则跳过;
3、不断重复2。
prime算法 1、选取一个点s(从该点开始构建树),初始化其余点到点s的距离
kruskal代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #define N 100010 #define M 200020 using namespace std; struct node { int x, y, z; bool operator < (const node &a) const{ return z < a.z; } }st[M]; int fa[N]; int find(int x) { return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);} int main() { int n, m, cnt, ans = 0; scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); cnt = n; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) fa[i] = i; for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) scanf("%d%d%d", &st[i].x, &st[i].y, &st[i].z); sort(st + 1, st + m + 1);//按权重升序排列 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { if(find(st[i].x) != find(st[i].y)) {//不是同一个连通分支,就加入此边 fa[find(st[i].x)] = find(st[i].y); --cnt;//记录加入边数,这里cnt初始为0,每次+1也OK ans += st[i].z; } } if(cnt > 1) printf("impossible\n");//最小生成树的边数应为n-1,n为结点数;或者可以遍历fa数组,求连通分支个数是否为1 else printf("%d", ans); return 0; }
prime代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std; const int N=1005; const int F=0x3f3f3f; int n,m,w[N][N]; void prime(){ int dis[N],ret=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) dis[i]=w[1][i]; bool vis[N]={false}; vis[1]=true; for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){//还有n-1个点没有加入树,循环n-1次 int cnt=F,p=-1; for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){//找到距离树最近的点 if(!vis[j]&&dis[j]<cnt){ cnt=dis[j]; p=j; } } if(p==-1){//有部分点是不连通的,建不了最小生成树 cout<<"impossible"<<endl; return; } vis[p]=true; ret+=dis[p]; for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ if(!vis[j]&&w[p][j]<dis[j])//更新其他点到树的距离 dis[j]=w[p][j]; } } cout<<ret<<endl; } int main(){ cin>>n>>m; memset(w,F,sizeof w); for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ int a,b,c; cin>>a>>b>>c; w[a][b]=w[b][a]=c; } prime(); return 0; }
7-3并查集【模板】 这道题的第十个测试点,如果用标准的并查集模板,时而过时而不过的,可以试试下面的快速读入方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N=10005; int f[N]; int find(int x){ if(f[x]==x) return x; return f[x]=find(f[x]); } void merge(int a,int b){ int x=find(f[a]),y=find(f[b]); f[x]=y; } int read() {//快速读入 int x = 0; char ch = getchar(); while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); return x; } int main(){ int n,m; n = read(); m = read(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) f[i]=i; while(m--){ int z,x,y; z = read(); x = read(); y = read(); if(z==1) merge(x,y); else{ if(find(x)==find(y)) cout<<"Y"<<endl; else cout<<"N"<<endl; } } return 0; }
7-4冗余连接 这道题也是考察在并查集,题目说找到最后出现的可以删除的边,所以可以从第一条边开始遍历,如果两个结点不在同一个连通分支,合并;如果在,那这条边是没用的,也就是我们要找的可以删除的边,用一个变量记录。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int f[110]; int find(int x){ if(f[x]==x) return x; return f[x]=find(f[x]); } void merge(int a,int b){ int fa=find(a),fb=find(b); if(fa!=fb) f[fa]=fb; } int main(){ int n; cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) f[i]=i; int p=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ int a,b; cin>>a>>b; if(find(a)==find(b)) p=i; else merge(a,b); } cout<<p; return 0; }
7-5求最短路径-flyod算法 这道题不算难,认真读题,flyod算法在其他数学规划题目中应用也很多,可以去了解一下。
思路:建图,求任意两节点间的最小距离
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; const int F=0x3f3f3f3f,N=11; int n,m,k; int mp[N][N]; int main(){ cin>>n>>m>>k; memset(mp,F,sizeof mp); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) mp[i][i]=0; while(m--){ int a,b,w; cin>>a>>b>>w; mp[a][b]=w; if(!k) mp[b][a]=w; } for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)//通过k点更新i与j的最小距离 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) mp[i][j]=min(mp[i][j],mp[i][k]+mp[k][j]); int mindis=F,p=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ int dis=0; for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) dis=max(dis,mp[i][j]);//求dis也可用dijkstra算法,令i为起点,不断更新其他点到i的距离 if(dis<mindis){ p=i; mindis=dis; } } cout<<p; return 0; }
7-6单源最短路径 dijkstra,迪杰斯特拉算法
这道题n比较大,但m很小,二维数组会爆内存,所以我们用两个vector数组分别存边的终点和权重。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <vector> using namespace std; const int F=0x3f3f3f3f; const int N=20005; vector<int> v[N];//边的终点 vector<int> w[N];//边的权重 int n,m; void dijkstra(int s){ bool book[N]={false}; int dis[N]; memset(dis,F,sizeof dis); for(int i=0;i<v[s].size();i++){//更新每个点到s的距离 dis[v[s][i]]=w[s][i]; } book[s]=true; for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){ int cnt=F,p=-1; for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ if(!book[j]&&dis[j]<cnt){//在剩余点中找距离s最近的点 p=j; cnt=dis[j]; } } if(p==-1) break; book[p]=true;//标记p点 for(int j=0;j<v[p].size();j++){//通过p点尝试更新其他点到s的最短距离 if(!book[v[p][j]]&&dis[p]+w[p][j]<dis[v[p][j]]) dis[v[p][j]]=dis[p]+w[p][j]; } } for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ if(dis[i]!=F) cout<<dis[i]<<" "; } } int main(){ cin>>n>>m; while(m--){ int a,b,c; cin>>a>>b>>c; v[a].push_back(b); w[a].push_back(c); } dijkstra(0); return 0; }
7-7有向图的拓扑排序 1、在有向图中选择一个没有入度的点输出;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <stack> const int N=1005; using namespace std; int n,m; vector<int> ve[N]; int count[N]={0}; void topo(){ stack<int> s;//采用栈存储入度为0的结点 int cnt=0;//计数 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!count[i]) s.push(i);//入度为0,入栈 } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){//每次输出一个点,故循环n次 if(s.empty()) break;//有环 int cur=s.top(); s.pop(); cout<<cur<<" "; cnt++; count[cur]=-1; //标记为-1,避免重复入栈 for(int j=0;j<ve[cur].size();j++){ int v=ve[cur][j]; count[v]--; if(!count[v]) s.push(v); } } if(cnt<n) cout<<endl<<"0"; } int main(){ cin>>n>>m; while(m--){ int a,b; cin>>a>>b; count[b]++;//计算入度 if(ve[a].size()) ve[a].insert(ve[a].begin(),b);//题目要求:表头插入法构造邻接表 else ve[a].push_back(b); } topo(); return 0; }
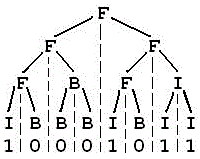
7-8FBI树
给定的字符串实际是二叉树的叶子结点,该二叉树的深度为n+1。
叶子结点在一维数组中的编号从2^n开始,通过叶子结点向上不断构造树。
这里使用一维数组构造树,如果不了解一维数组如何构造二叉树的话,可以到CSDN上学。
这里采用的是边构造边遍历的方式。也可以先构造二叉树,再后序遍历。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int n; char t[3000]; void dfs(int root){//从树的根结点1开始后序遍历 if(root>=(1<<n)){//到达叶子结点这一层也就是最后一层就没必要再往下了,输出结点值,return; cout<<t[root]; return; } dfs(root*2);//后序遍历左子树 dfs(root*2+1);//后序遍历右子树 if(t[root*2]=='I'&&t[root*2+1]=='I')//根据左右子树构建根结点 t[root]='I'; else if(t[root*2]=='B'&&t[root*2+1]=='B') t[root]='B'; else t[root]='F'; cout<<t[root];//后序遍历根结点 } int main(){ cin>>n; getchar(); for(int i=0;i<(1<<n);i++){ int p=getchar()-'0'; if(p) t[(1<<n)+i]='I';//存储叶子结点,二叉树第n+1层,1<<n是2^n,也可写pow(2,n); else t[(1<<n)+i]='B'; } dfs(1); return 0; }
7-9堆的操作 考察小根堆,下面代码有部分注释,如果想细节学习,可以到CSDN上了解一下,或者找群内管理员。
自写函数(原理部分) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; int heap[2010],heap_size; void siftdown(int i){//向下寻找正确位置 while(i*2<=heap_size){ int ch=i*2;//小根堆满足父结点小于等于子节点,也就是说小于等于值最小的那个结点才可以,所以下面加一句判断 if(ch+1<=heap_size&&heap[ch+1]<heap[ch]) ch++; if(heap[i]<=heap[ch]) break;//当前位置已满足,退出循环 swap(heap[i],heap[ch]);//不满足,则将父结点与子节点交换 i=ch;//继续向下找合适位置 } } void push_data(int data){//向堆内插入结点 int cur=++heap_size; heap[cur]=data;//先放到堆的最末端 while(cur!=1&&heap[cur]<heap[cur/2]){//向上寻找正确位置 swap(heap[cur],heap[cur/2]); cur/=2; } } void pop_data(){//移除堆顶 if(!heap_size) return; heap[1]=heap[heap_size--];//将最后一个结点放到首端,堆长度-1 siftdown(1);//向下寻找正确位置 } int main(){ int n,k; cin>>n>>k; while(k--){ int p,x; cin>>p; if(p==-1) pop_data(); else{ cin>>x;//记得判断堆的容量,题目规定容量为n if(heap_size<n) push_data(x); } for(int i=1;i<=heap_size;i++){ if(i>1) cout<<" "; cout<<heap[i]; } cout<<endl; } memset(heap,0,sizeof heap); int m; cin>>m; heap_size=m; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) cin>>heap[i]; for(int i=m/2;i>=1;i--) siftdown(i);//从数组中间位置开始调整 for(int i=1;i<=heap_size;i++){ if(i>1) cout<<" "; cout<<heap[i]; } return 0; }
c++自带函数 (1)make_heap将一个可迭代容器变成堆,默认大根堆
make_heap(begin,end,less<>());//大根堆
(2)push_heap在堆的基础上进行插入,要求前面的区间满足堆结构
第一步将插入数据放到容器末尾
(3)pop_heap将第一个元素和最后一个元素交换位置,对前n-1个元素构造堆
push_heap(begin,end,greater<>());
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <functional> using namespace std; int main(){ int n,k; cin>>n>>k; vector<int> ve; while(k--){ int p,x; cin>>p; if(p==1){ cin>>x; if(ve.size()<n){//记得判断 ve.push_back(x); push_heap(ve.begin(),ve.end(),greater<>());//在堆的基础上进行插入 } } else{ pop_heap(ve.begin(),ve.end(),greater<>());//删除堆顶 ve.pop_back();//删除末尾元素 } for(int i=0;i<ve.size();i++){ if(i) cout<<" "; cout<<ve[i]; } cout<<endl; } int m,t; cin>>m; vector<int> v; while(m--){ cin>>t; v.push_back(t); } make_heap(v.begin(),v.end(),greater<>());//构造小根堆 for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){ if(i) cout<<" "; cout<<v[i]; } return 0; }
7-10哈夫曼编码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <map> using namespace std; const int MAX=400; typedef struct{ int weight; int parent; int Lchild; int Rchild; }HTNode,*HuffmanTree; typedef char** HuffmanCode; void select(HuffmanTree ht,int n,int *s1,int *s2){//选择两个weight最小的节点 int min1=MAX,min2=MAX; *s1=0; *s2=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!ht[i].parent){ if(ht[i].weight<min1){ min2=min1; *s2=*s1; min1=ht[i].weight; *s1=i; } else if(ht[i].weight<min2){ min2=ht[i].weight; *s2=i; } } } } void create(HuffmanTree ht,int n){//建树 for(int i=n+1;i<=2*n-1;i++) //非叶节点初始化 ht[i].weight=ht[i].parent=ht[i].Lchild=ht[i].Rchild=0; int s1,s2; for(int i=n+1;i<=2*n-1;i++){//创建非叶节点 select(ht,i-1,&s1,&s2);//选择两个weight最小的节点,合为一棵树 ht[i].weight=ht[s1].weight+ht[s2].weight; ht[s1].parent=i; ht[s2].parent=i; ht[i].Lchild=s1; ht[i].Rchild=s2; } } void code(HuffmanTree ht,HuffmanCode &hc,int n){//编码 char *cd=new char[n]; cd[n-1]='\0'; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ int start=n-1,c=i,p=ht[c].parent;//从叶子结点到根,逆向求编码,c为当前节点,p为c的父结点 while(p){ --start;//逆序存储 if(ht[p].Lchild==c) cd[start]='0';//左孩子记0 else cd[start]='1';//右孩子记1 c=p;//向上编码 p=ht[p].parent; } hc[i]=new char[n-start];//申请空间并存储该字母的哈夫曼编码 strcpy(hc[i],&cd[start]); } free(cd); } int main(){ string str; while(cin>>str){ map<char,int> mp; for(int i=0;i<(int)str.size();i++){ mp[tolower(str[i])]++;//统计出现次数 } int n=mp.size(); HuffmanTree ht=new HTNode[2*n]; HuffmanCode hc=new char* [n+1]; int i=1; for(auto it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++,i++){//[1,n]存放叶子结点,初始化 ht[i].parent=ht[i].Lchild=ht[i].Rchild=0; ht[i].weight=it->second; it->second=i;//标记每个字母在哈夫曼树中对应的位置,便于后续输出 } create(ht,n); code(ht,hc,n); for(int i=0;i<(int)str.size();i++){ cout<<hc[mp[tolower(str[i])]]; } cout<<endl; } return 0; }